The Differences Between Diabetes 1 and 2

The Centers for Diseases and Prevention (CDC) describe diabetes as a chronic (long-term) health condition that affects your body's ability to convert food into energy.
Diabetes has two main types— Type 1 and Type 2. However, most people are unaware of their differences. Diabetes type 1 and type 2 are both chronic diseases that affect the body's ability to regulate blood sugar levels. They also cause excessive blood sugar levels since they neither properly produce enough insulin nor utilize it. Their issues are similar, but their causes and treatments differ.
In this article, you'll learn the differences between diabetes 1 and 2.
What is Type 1 Diabetes?
According to the
American Diabetes Association, about 244,000 children and adolescents have type 1 diabetes. Compared to type 2 diabetes, type 1 diabetes occurs ten times less often. The condition involves an autoimmune response that attacks the cells that make insulin in your pancreas, caused by your genes or the environment. In short, a person with Type 1 diabetes has insufficient or low insulin levels in the body. Your body uses insulin to metabolize sugar. Blood sugar cannot get into cells if insulin isn't present. Moreover, juvenile diabetes or insulin-dependent diabetes are other names for Type 1 Diabetes.
What is Type 2 Diabetes?
Diabetes type 2 is a long-term (chronic) condition that leads to high blood sugar levels. With type 2 diabetes, your body still produces some insulin, but it is not enough. In this case, the pancreas cannot account for high blood sugar levels due to poor diet and lack of exercise.
A type 2 diabetic's body's cells begin to resist insulin. With this, cells cannot absorb glucose. As a result, it accumulates in the blood and cannot enter cells without increased insulin levels; this is known as insulin resistance.
It is more likely to affect middle-aged and older people. Obesity in childhood can also lead to type 2 diabetes in kids and teens. Furthermore, approximately 29 million Americans have type 2 diabetes, formerly known as adult-onset diabetes.
Diabetes Type 1 vs. 2
The difference between type 1 and type 2 diabetes is that type 1 diabetes is a genetic disease that often appears in childhood. When you have type 1 diabetes, your immune system destroys insulin-producing cells in your pancreas. In contrast, type 2 diabetes is mainly caused by diet and develops over time.
Fortunately, people with type 1 diabetes can manage their condition today and still lead a normal life despite the disorder.
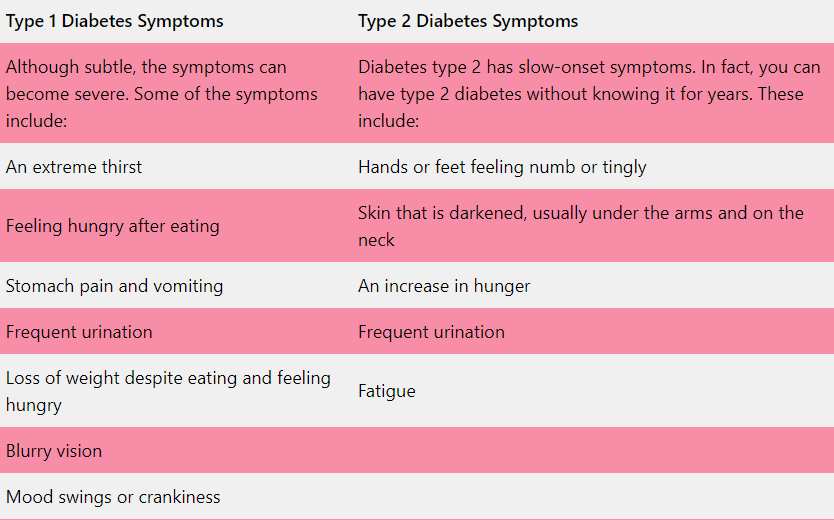
What are the risk factors for type 1 and type 2 diabetes?
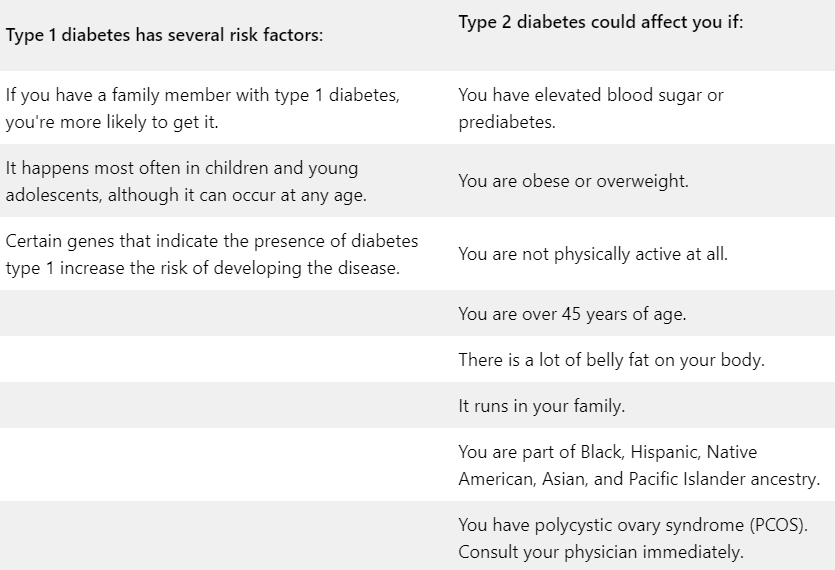
Causes of Type 1 Diabetes
In type 1 diabetes, a person's immune system misidentifies healthy cells for foreign invaders. This happens when the immune system activates and attacks insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. Once these beta cells are destroyed, the body cannot produce insulin.
It's not known why the immune system attacks the body. Virus exposure could be a factor, as well as genetics.
Causes of Type 2 Diabetes
Those with type 2 diabetes have insulin resistance. However, the body still produces insulin but cannot use it properly. When your body cannot properly use insulin, glucose builds up in your bloodstream.
There is no apparent reason why some people become insulin resistant and others don't, but being overweight and inactive may contribute. A person's genes and environment may also play a role.

Can Type 2 Diabetes Become Type 1?
There is no way for type 2 diabetes to turn into type 1 diabetes. Despite receiving a diagnosis of type 2 diabetes, a person may later receive a separate diagnosis of type 1. Typically, doctors initially suspect that an adult with diabetes has type 2 since it's the most common type.
Is Type 1 or Type 2 Diabetes Worse?
Diabetes type 2 is typically milder than type 1. But, it can still cause serious health complications, particularly in small blood vessels found in the kidneys, nerves, and eyes. It also increases the likelihood of heart disease and stroke.
Does type 1 diabetes require insulin?
Type 1 diabetic patients cannot produce insulin in their bodies, so they must inject it regularly. Aside from insulin injections, some people use insulin pumps. Insulin pumps deliver a constant supply of insulin to the body using a tube.
Blood sugar testing is essential because sugar levels can fluctuate quickly with type 1 diabetes.
How to manage type 2 diabetes?
Combining diet and exercise is often enough to control and even reverse type 2 diabetes. Your doctor may prescribe you medications if lifestyle changes aren't sufficient to improve your body's ability to use insulin.
Blood sugar control is essential for managing type 2 diabetes as well. So, check your blood sugar more often. Moreover, your doctor may prescribe insulin injections for high blood sugar levels.
The Right Care Can Manage Diabetes
Whatever type of diabetes a person has, they must closely follow up with their primary healthcare provider. Having diabetes can result in devastating complications, including blindness, kidney failure, amputation, heart attacks, strokes, and even mortality. Keeping blood sugar levels within a healthy range is crucial.
Our doctors at
Houston Family Practice have years of experience providing vital early detection services. Health-conscious individuals can take advantage of our convenient screenings. We look forward to serving you!
Send US A MESSAGE
Drop us a line!
We will get back to you as soon as possible.
Please try again later.
Our goal is to make you feel better as quickly as possible. We are proud to provide a high quality level of customer service, medical experience, and commitment to health and wellness to all our patients.
Quick links
Contact us
Our experienced medical professionals put your healing needs first. We are proud to provide a high quality level of customer service, medical experience, and commitment to health and wellness to all our patients. Our goal is to make you feel better as quickly as possible.
Quick links
Contact us
HOUSTON FAMILY PRACTICE | All Rights Reserved.